In the last few years, Computer Aided Design has evolved in a very rapid way, so many pieces of software have been made to fulfill the market’s needs. Today, we will try to give you a detailed comparison between two of the most known software in the field so you can decide which one suits you the best before purchasing it.
CATIA vs Inventor: key differences and similarities
Pieces of CAD software are multiple. And every single program provides many features and tools. As a user, it may be confusing to choose which one is better, especially if you are a beginner. This is where comparison articles come in very handy.

You can check our comparison list from here:
When it comes to CATIA and Inventor, these two pieces of software are both leaders in the three-dimensional designing world. They are used by several industries, but they have a great deal of non-similarity that makes them almost incomparable.
Let’s start by having an overview of both CATIA and Inventor.
What is CATIA?
CATIA (Computer Aided Three-dimensional Interactive Application) is a multiplatform CAD, CAM, and CAE commercial software suite developed by French Dassault Systemes. This software was developed to use in different industries and to design all types of rich and complex designs.

Official website: CATIA
What is Inventor?
A computer aided three-dimensional software that is provided by Autodesk. It is highly recommended by designers because the company tried to make it on a level where prototyping would be like a piece of cake, especially for beginners. It makes all products’ life cycles easy to be generated in no time and with no cost or physical machining until everything is finally tested on the software and approved.

Official website: Inventor
1. Modeling
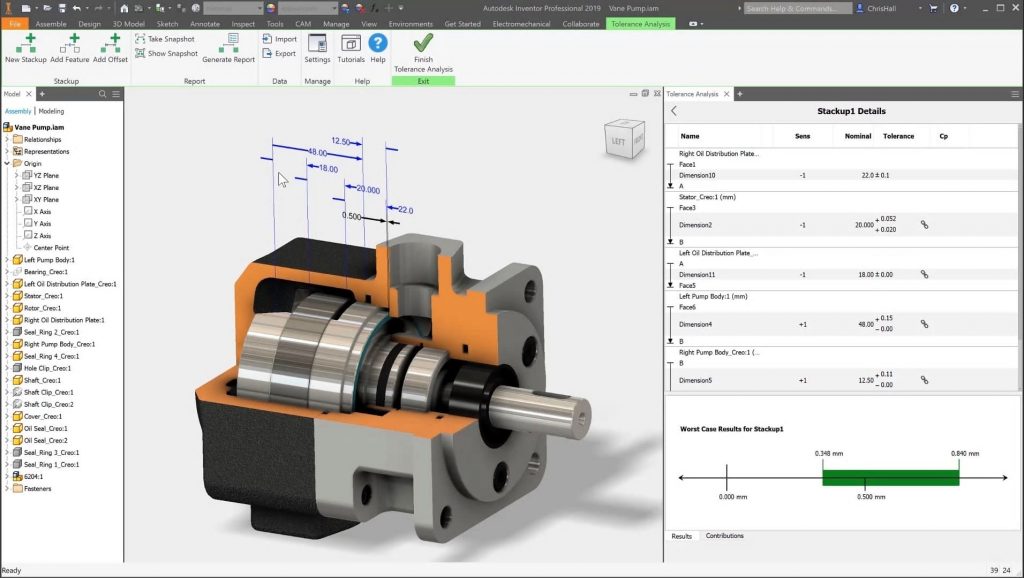
Inventor provides catalogs of standard mold bases and components so you won’t have to spend time modeling them. You can create a wide range of complex geometries by easily combining solids and surfaces. It gives you precise control of shape characteristics, advanced modeling tools, and manufacturing ready-to-use parts.
Working with parts that are based on mechanical relationships rather than on geometric descriptions (lines, arcs, and circles), allows you to stay away from constraints, working with much freedom on 2D drafting and 3D modeling as well as accelerating your work.

On the other hand, CATIA has better surface modeling modules. Maybe, the best in 3D CAD market! It has more advanced surfacing workbenches for conceptual modeling and class-a modeling, which you will not find in Inventor. It is much easier to use and more powerful. Modeling in CATIA takes less time.
2. Animation
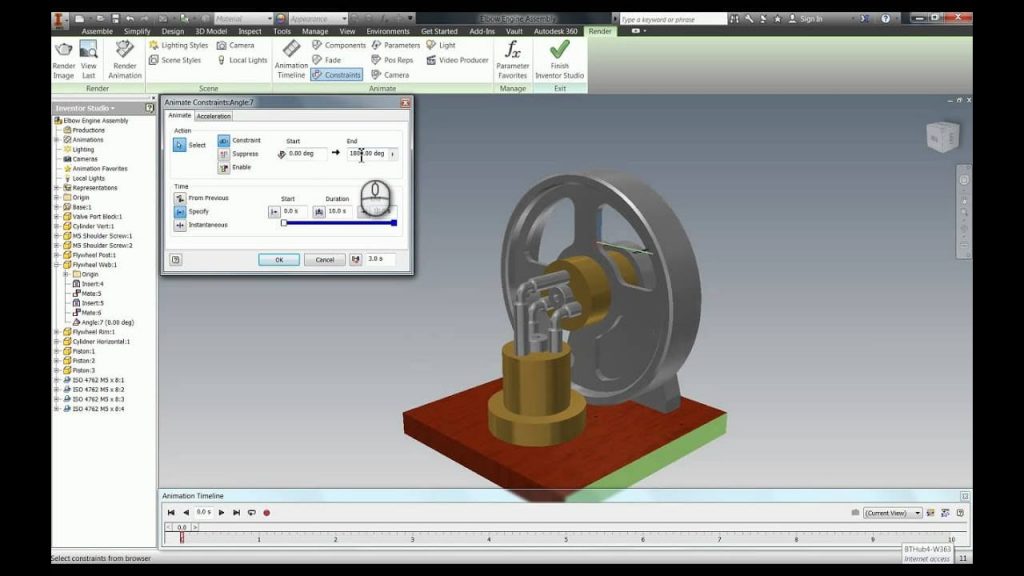
With very limited animation and almost no real world physics capabilities, Inventor software provides animated visualizations of the 3D model. With the analysis output, the user can select different ways to view results to make it easier to understand and visualize complex problems. That way, you can focus on specific components of the design to see how they appear.

CATIA does a better job with the physics, but if the users hope for a fully animated model, they will require another piece of CAD software.
3. Simulation
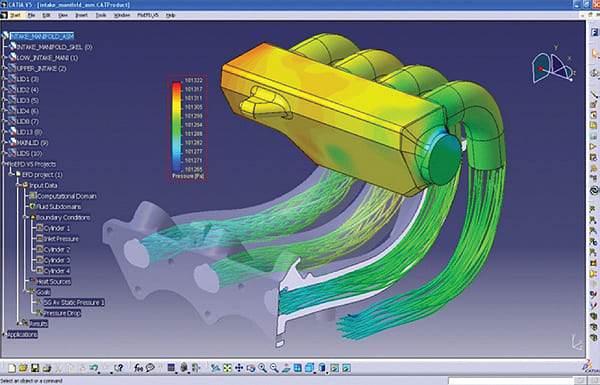
You don’t need to be a simulation expert to effectively simulate and optimize designs digitally. Their easy-to-use and tightly integrated motion simulation and stress analysis in both software help the designers predict how their design will work in real-world conditions before building it. That helps to quickly understand the design’s behaviors, including the position, velocity, and accelerations of the moving parts.
4. Rendering
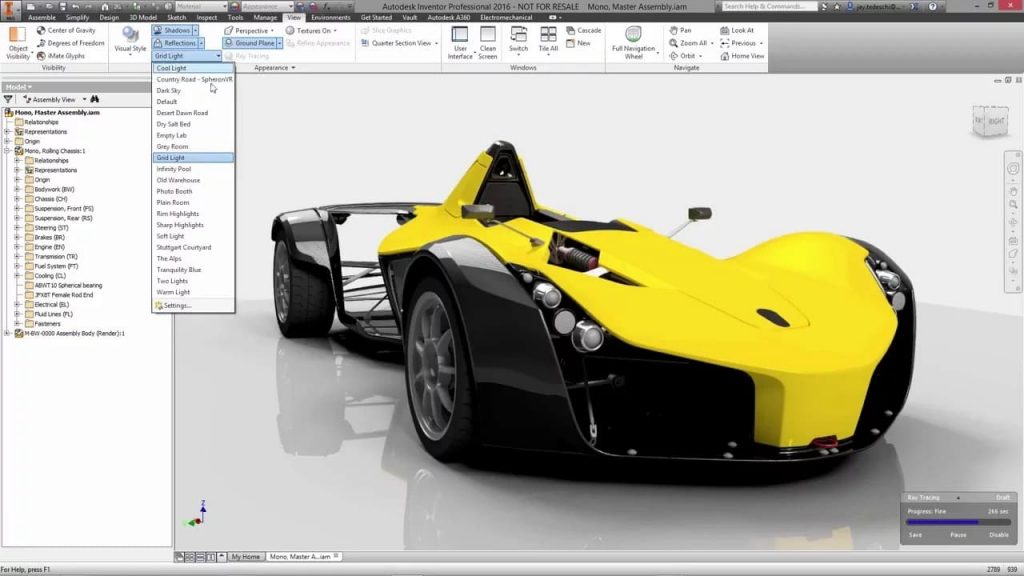
With the power of modern desktop computers and the advanced rendering features included with Inventor and CATIA software, it’s easy to create realistic images and videos that permit people without engineering experience to understand engineering illustrations to eventually visualize the design. And even without the hardware, online render farms and services can do the trick.
These pieces of software eliminate the high costs of prototyping and 3D printing, and product photography with high-quality photorealistic renderings and animations. They provide design engineers with tools they need to quickly create renderings and animations.
5. Design and 2D drafting

These pieces of software products include an intuitive parametric design environment for developing initial concept sketches and kinematic models of parts and assemblies. They automate the advanced geometry creation of intelligent components, such as plastic parts, steel frames, rotating machinery, tube and pipe runs, electrical cable and wire harnesses, not to mention their high-productivity 2D drafting tool.
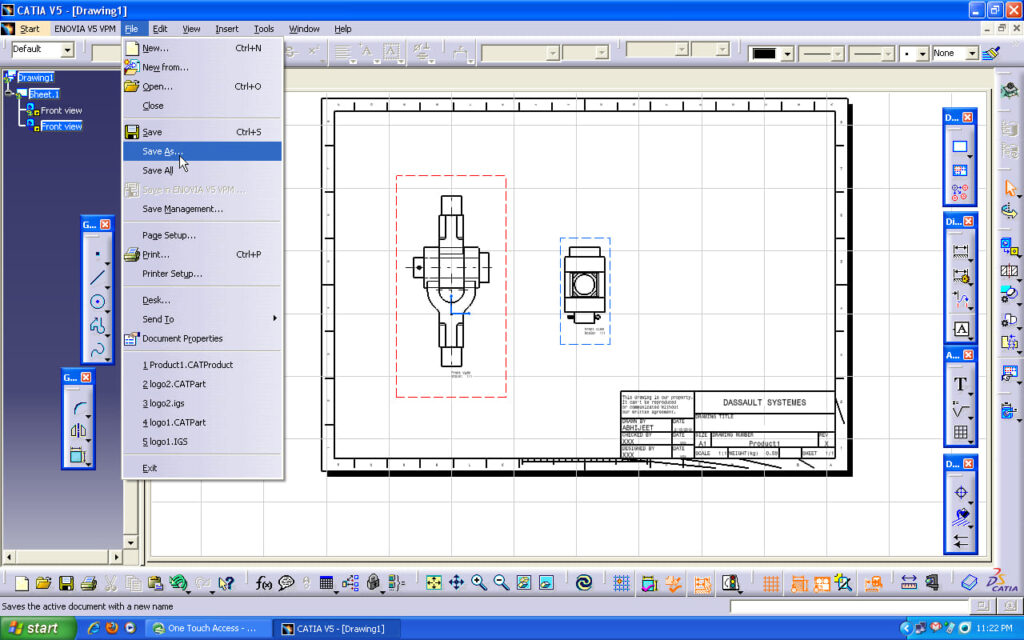
These pieces of software reduce the geometry burden so that engineers can rapidly build and refine digital prototypes that validate design functions and help minimize manufacturing costs.
6. Industries and use cases
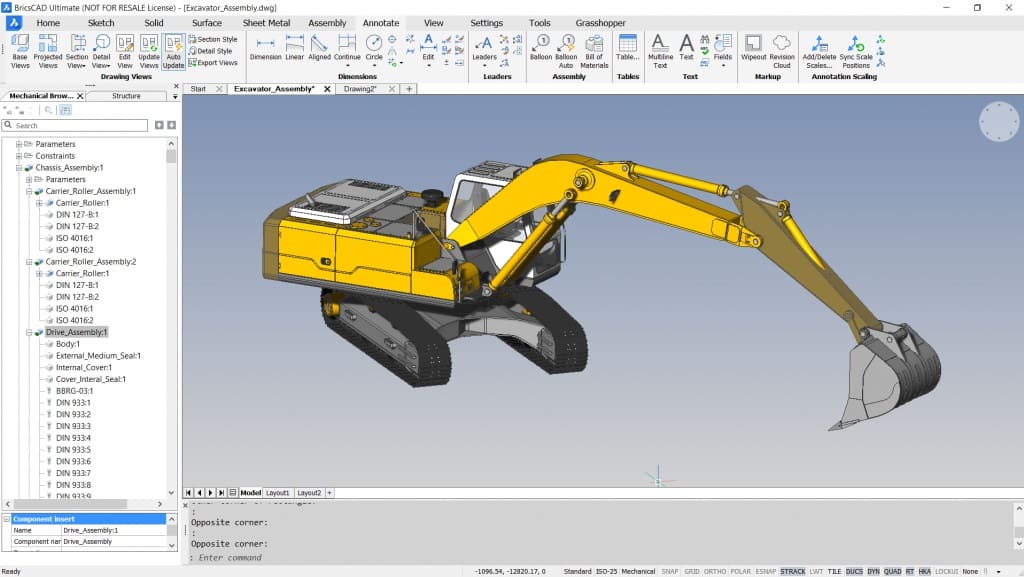
Inventor is the kind of software that was developed to be used by all kinds of designers, from smaller industries to big ones because of the many features it provides. CATIA, on the other hand, is more a high-scale production specialty; it was mainly segmented through aircraft manufacturers and all types of big industry that can actually afford its pricing.
7. Learning curve

Both pieces of software are user-friendly with a simple interface where you can find tools easily. Inventor eliminates the interruptions that prevent you from making progress. The command you need shows up right at your cursor. And you can easily make changes without having to hunt for the right feature or fight with existing geometry and constraints.
But in CATIA, you won’t find similar tools grouped in one row as in Inventor, which makes it a bit more time-consuming for novice designers, but once you get familiar with it, it will become easier. So, they don’t actually take so much time to learn them because you can find all necessary data online with tutorials or even reviews, which makes the process less troubling.
8. System requirements
CATIA and Inventor both run on Windows.

System requires for Inventor
- Recommended: Microsoft® Windows 7 64 bits avec Service Pack 1 or Windows 8.1 or Microsoft Windows 10
- Minimum: Microsoft Windows 7 64 bits avec Service Pack 1
System requires for CATIA
- Microsoft Windows 7 or Windows 10 (64-bit)
- Multi-core, 64-bit processor (ex. Intel i5, i7 or Xeon)
- Dedicated graphics card recommended (not integrated on motherboard such as Intel Integrated graphics)
- 4GB of RAM – 8GB or more is highly recommended
- 10GB Free Hard Disk space
- Microsoft Office 2013 or newer for report generation

Lastly, we can just add a small note on CATIA’s evolution, which has been very slow compared to Inventor’s. Major revisions only occur once or twice a decade with only service upgrades in between. When they launch a new version, the difference is so striking that it looks like a whole new application. The more consistent progression of Inventor’s annual releases makes it easier to stay continually productive, especially with the rate of change of both products.
9. Licensing and pricing

This is the first and the greatest difference between them! Inventor is very cheap compared to CATIA. Even its lowest cost licenses have a big variety of features that makes it possible to get your work done. Not to mention the high-cost license for professionals and big companies, which is also cheaper than CATIA’s.

Inventor provides the free trial unlike CATIA, but both pieces of software provide the student license, which is the cheapest one with the fewest features possible. CATIA is more expensive (base, standard versions) however, it offers a lot of features!