3D design is not only used in creating games; it is also used in several fields like industry. The relation between 3D design and industry has gone a very long way before even the creation of computers. It was where engineers used to draw their designs on paper from different views to make the first prototypes.
The reason why I wrote this article is to take you on an interesting and different experience, showcasing the best 3D Industrial design software.
How to choose the best 3D industrial design software for you?
Nowadays, the process has become more and more simple thanks to technological innovation, which resulted in new specialized software. Therefore, the use of Computer Assisted Design software and Computer Assisted Manufacturing programs has become crucial for all kinds of production. But the question is: how to choose the one that suits YOU?
We recommend you take these 3 main factors into consideration:
- The intuitiveness and the efficiency of the User Interface, because it directly effects your productivity, workflow and production.
- The overall affordability, especially depending on whether you’re a hobbyist, amateur or professional.
- The level of compatibility and integration with other tools that you use (like addons, plugins, rendering engines…, etc.)
7. Solid Edge
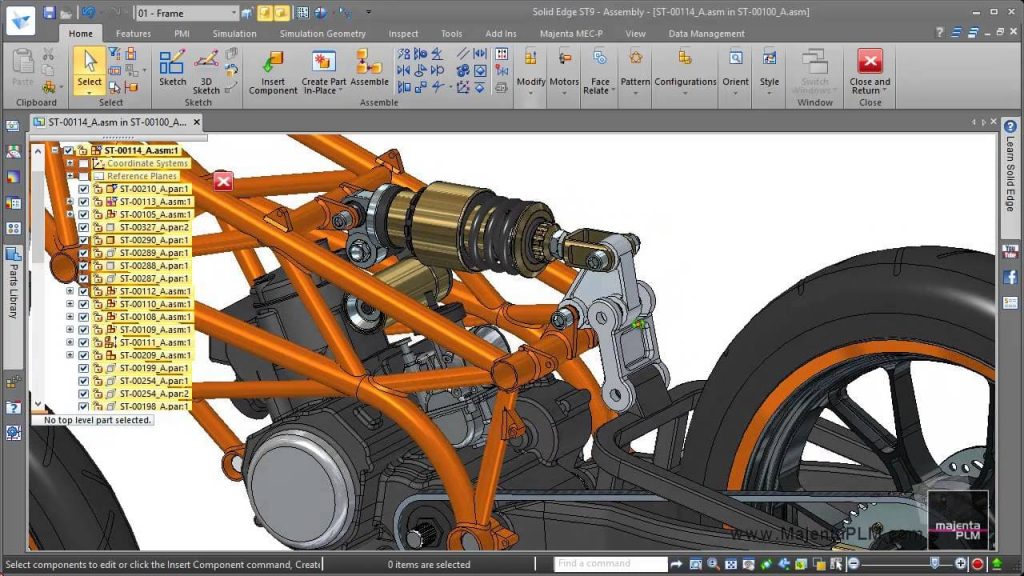
Released in 1996 by Intergraph. Solid Edge is another veteran on the CAD market. It was acquired in 2007 by Siemens, which has been eager to continue its development.
You might think that Solid Edge would overshadow NX; however, these two programs do not aim at the same target.
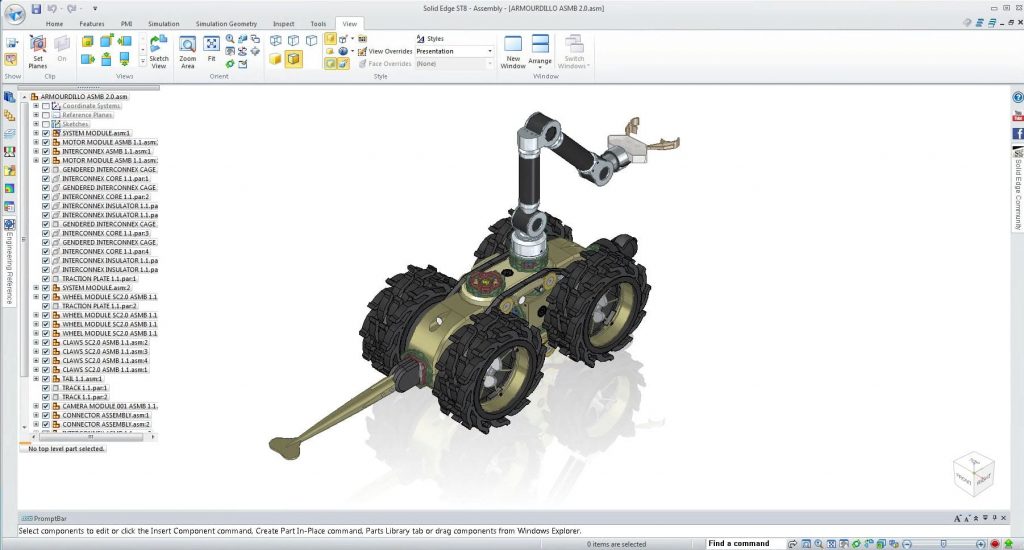
Solid Edge is easy to learn; its features are more accessible, and it costs much less than NX. In other words, it’s a good compromise between flexibility and ease of use in addition to affordability. On the other hand, Solid Edge offers the same integration with PLM solutions as well as CAM and CAE functionalities.
The software is best known for its synchronous technology: a technique that combines parametric modelling and direct modelling, which is more accessible. It offers a simple tool, but still allows the high level of control of modelling. But of course, You can also choose to work only with parametric or direct modelling.
Link: Solid Edge
6. NX
Developed by the industrial manufacturing giant Siemens. NX, previously known as Unigraphics, is one of the best professional 3D industrial design software available today.
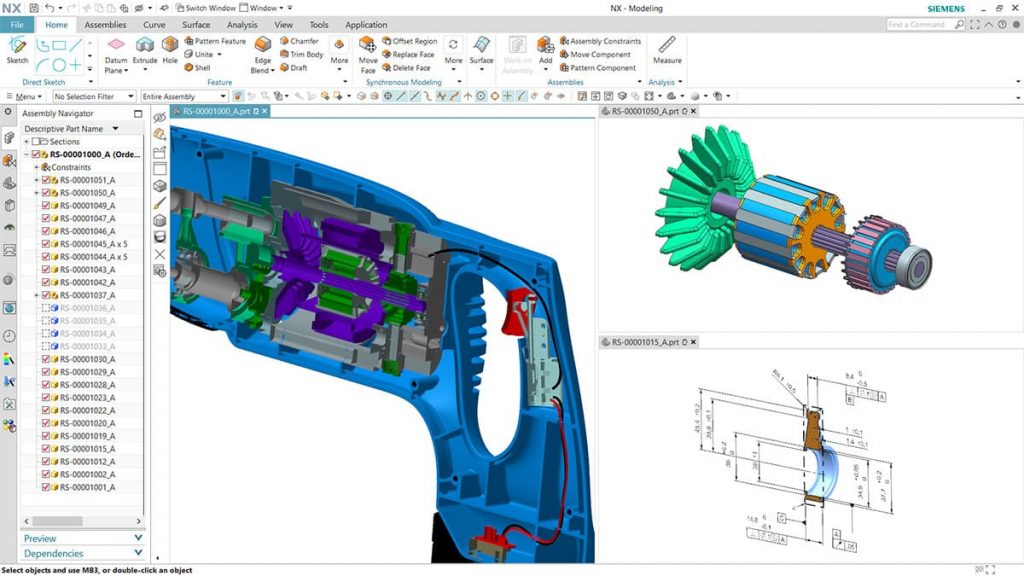
NX is based on industry-leading parametric, direct, and surface modelling tools. It integrates seamlessly with Siemens’ Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) functions. This compatibility facilitates collaboration for work, involving several teams of engineers and it also allows you to keep valuable documentation on project development.
On a more technical level, NX offers comprehensive functionality for analyzing the structural integration of a part to determine the functional capacity of a finished product, such as its durability.
With such a range of tools, NX applications go beyond what other CAD software can offer, such as the development of proofs of concept.
NX is a benchmark among many industries, especially in the automotive industry where it is used by General Motors, Fiat Chrysler, Nissan, and Suzuki.
Link: NX
5. Creo
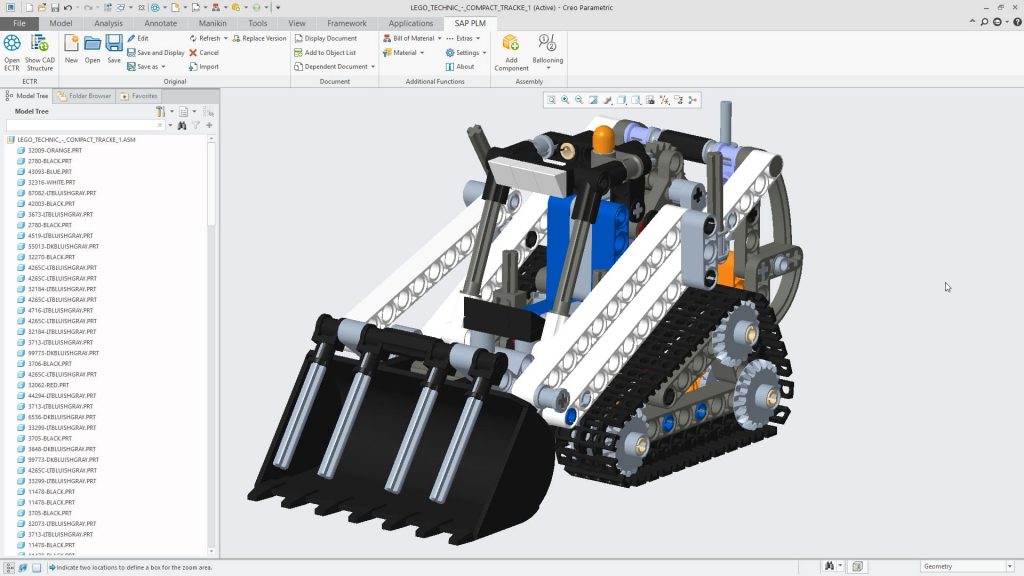
Creo View is a complete digital model visualisation review tool. It gives you all the control to consult, visualize, annotate, measure, section, as well as to design the product from a mechanical point of view with Creo View MCAD and electronic point of view with Creo View ECAD. The use cases of Creo can vary greatly.
Creo View MCAD makes it easy to take a global view of the product and provide a good overview of the engineering design. 3D data from major MCAD tools is supported besides drawings and documents from a multitude of sources.
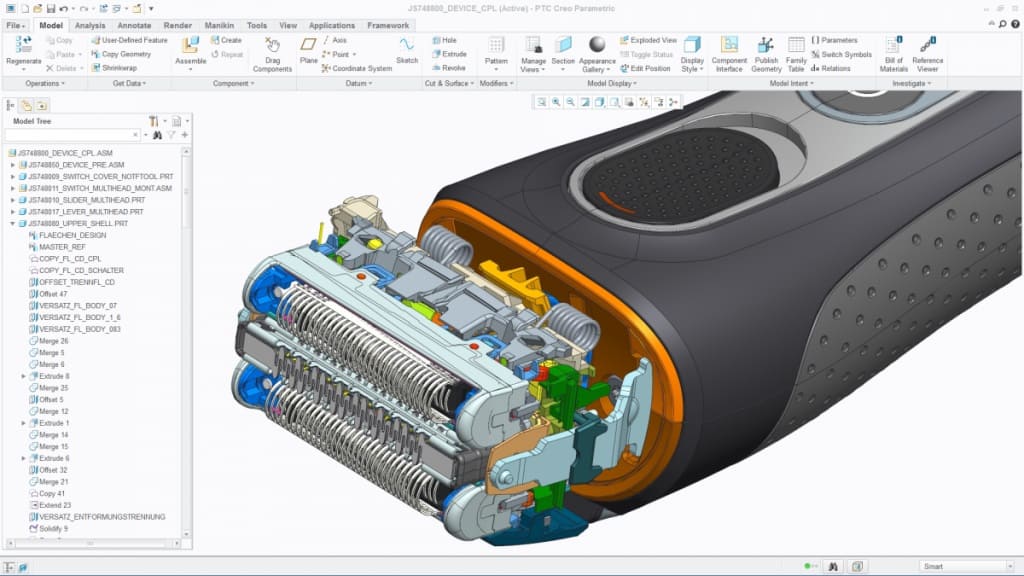
You also can have fast access to complex information, reducing work effort and improving decision making. Because Creo View ECAD and Creo View MCAD operate the same infrastructure, users of these two applications can perform unique functions, such as cross-searches between ECAD / MCAD abstractions.
With Creo View MCAD, you can easily carry out your project reviews and digital models by visualizing, measuring, annotating and exporting your information.
Link: Creo
4. AutoCAD
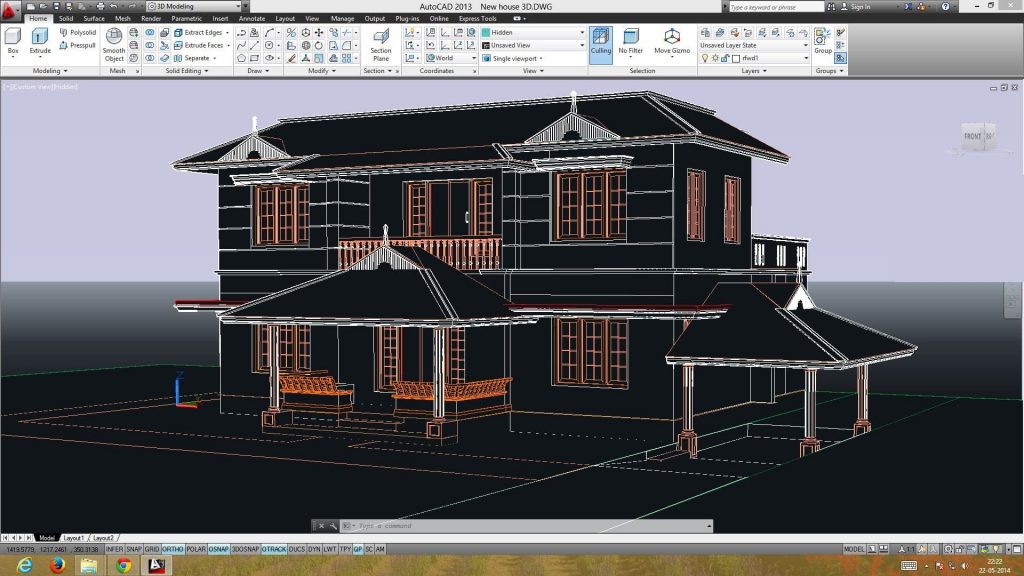
AutoCAD is a computer drafting software for architectural professionals and engineering students. It is a pioneering program for the representation of CAD technology, with which we can make drawings, plans, and documents of all kinds of engineering projects. The use cases of AutoCAD can really surprise you.
By using this tool, we can draw and edit 2D geometries and 3D models with solid faces, surfaces, and all kinds of mesh objects. Text annotations can be added in drawings, dimensions, guidelines and tables, as well as customize tasks and complementary applications.
With AutoCAD, we can work using vector-type images in addition to being able to import other types of files such as bitmap, which gets you to a dynamic process.
The program is responsible for using a system of layers, which allows modelling work with greater freedom, organizing all the elements that will make up our plan that we are developing.
Link: AutoCAD
3. Inventor
It’s another program developed by Autodesk. It offers various modelling tools (parametric, direct, and free), resources, and simulation functionalities in a very complete package.
This 3D industrial design software is considered to be somewhat more user-friendly than its competitors, and for this reason, it is commonly used by designers with no engineering background.
However, Inventor is a powerful tool. It was indeed designed for professional use, especially for architecture and product design.
It is well-established software in the industry; it has been in the market for over 20 years, competing with other well-known options like SolidWorks.
Link: Inventor
2. CATIA
CATIA is the world’s number one 3D software for industrial design and experience. It is highly adopted by the most important companies in various industries to develop the products that we see and use every day.
With CATIA it is possible to model any product based on its actual behavior. System architects, end engineers, designers, building professionals, and all contributors can define, imagine, and shape the connected world.
Link: CATIA
1. SolidWorks
This 3D industrial design software is a parametric 3D modelling and computer-aided engineering (CAE) tool that works only on Windows. Now, it is developed and edited by the French company Dassault Systèmes (3DS).
It is without a doubt one of the most popular 3D modelling programs on the market. Unlike other products, SolidWorks’ power resides in the fact that it was designed for a wider range of industries, including shipbuilding, industrial equipment, architecture, and modelling.
We made several full comparisons with other software to help you choose the one that suits your needs the most:
- Solidworks and Onshape.
- Solidworks and Fusion 360.
- Solidworks and FreeCAD.
- Solidworks and Rhino.
- Solidworks and CATIA.
- Solidworks and AutoCAD.
On the official website of SolidWorks, you will find a search engine that gives you access to more than 500 plugins. They can help you gain time and reduce effort.
- Power surfacing.
- CST plugin.
- The exact flat.
SolidWorks has multiple functions, drawing, modeling, and assembling. You just need a couple of days to learn the basics of the software, and it might require modelling training to get the most out of its potential.
Link: SolidWorks
Conclusion
In the end, I really hope that this article was useful and that now you have a glimpse of the variety of uses of these 3D industrial design software.
These above mentioned are mostly paid (and quite expensive too). You can check our list of free alternative industrial design software that you can use online, without breaking the bank.