If you’re interested in 3D printing, you may have heard of Blender – a popular 3D modeling software that can be used for 3D modeling, sculpting, animation, texturing, rendering and so much more. But you must be wondering: is Blender good for 3D printing?
Long story short and after recent updates, you can now use it to do a lot of cool things in many different industries. Such as manufacturing, medicine, architecture, entertainment, and design.
Table of Contents
In this article, we’ll explore the ways that Blender can be used for 3D printing, the benefits and drawbacks of using this software, and what you need to know to get started.
3D printing definition
First, let’s review what 3D printing is and how it works. 3D printing is a process of creating physical objects from a digital model. This is done by slicing the digital model into thin layers, and then printing each layer one at a time until the object is complete. 3D printing can be used to create everything from small household items to large-scale industrial prototypes.

How to use Blender for 3D printing in 6 easy steps
The history of 3D printing goes way back to the 1980s, and 3D printing in Blender specifically was possible since 2002. However, when Blender version 2.67 was released, it became even more accessible and powerful than ever before.
One of the key advantages of using Blender is its flexibility – it can be used to create models for a wide range of 3D printers, from hobbyist machines to industrial-grade equipment. It’s all thanks to the 3D Printing Toolbox, real-time Mesh Analysis features and so on and so forth.
Here are simple steps for a successful 3D printing using Blender:
- Start by creating a new project in Blender and select the units of measurement that match the requirements of your 3D printer. This will ensure that your model is the correct size for printing.
- Use Blender’s modeling tools to create your 3D model. Keep in mind that your model must be “watertight,” meaning that it is a solid object with no holes or gaps.
- Once your model is complete, you need to export it in a file format that is compatible with your 3D printer. The most common file format for 3D printing is STL (Standard Tessellation Language).
- Before exporting, make sure to check your model for errors or issues that could cause problems during printing. Blender has a built-in 3D printing add-on that can help you identify and fix these issues.
- When exporting your model, make sure to set the correct units and scale for your 3D printer. You may also need to adjust other export settings, such as the mesh resolution or number of triangles, depending on your printer’s requirements.
- Finally, import the exported STL file into your 3D printing software and prepare it for printing by setting up the print bed, adjusting the print settings, and generating the G-code file that will control the printer.
Send the G-code file to your 3D printer and start the print job. Be sure to monitor the progress of the print and make any necessary adjustments to ensure a successful print. Check our video above for more details!
By following these steps, you can create 3D models in Blender and use them for 3D printing with confidence.
Types of 3D printing models
3D printing organic models

For the most part, if you want to 3D print organic forms such as characters, animals, monsters or anything else that does not represent a solid surface, Blender is a great option. This also includes organic shapes in 3D models such as sofas, pillows, trees, and other artistic design shapes.
Some of you might argue that it’s not as intuitive and easy compared to 3D printing CAD software, but you can find a wide variety of awesome Blender modeling addons that can help you bridge the complexity gap.
3D printing hard surface models
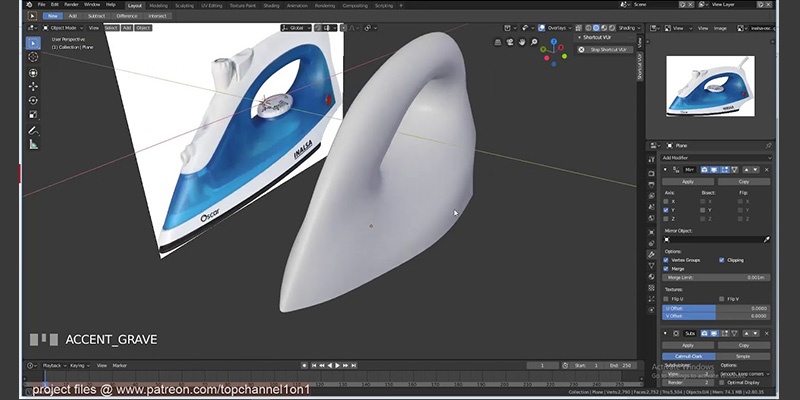
When it comes to 3D printing industrial parts for mechanical engineering, industrial manufacturing, architecture or design, the most important problem that you will face is the tricky nature of accurate measurements in 3D packages like Blender.
In terms of modeling 3D hard surface models, Blender is still considered one of the best 3D software though. However, if you want to take it to the next level, you can use some fantastic specialized hard surface modeling addons that can help you be more accurate. Also do more by saving time and energy.
Tips to prepare models for printing in Blender
Once you are done modeling, 3D printing from Blender has a preliminary phase. If you want to make sure that everything is going to work fine, Blender files often need little fixes before sending them to the printer. Here are a few tips to perform it successfully:
- If you have a model created from several objects or meshes, first make sure that each individual mesh is manifold (also know as a water-tight 3D model). Because it is not going to be printed correctly or not at all if this is not the case.
- Since the mesh of the 3D model is defined by edges, faces, and vertices, it has to be manifold. If it is a non-manifold mesh, it means there are errors in the 3D model that cannot define with precision the geometry of the 3D model. Otherwise the 3D file will not be recognized by the 3D printer, and consequently, the 3D model will not be printed.
- Your model should be one piece, not a collection of separate pieces that are not really welded together. Once you’ve got all your meshes manifold, make sure that every mesh is its own object.
Additionally, there are programs that can help fix your files too, such as MeshLab, Meshmixer and NetFabb. Not to mention that if you use a service like Shapeways, they will fix your files automatically before sneding them to print.
Blender vs other 3D Printing Software
Compared to specialized CAD software that architects and engineers use for designing mechanical or any other functional parts that actually work in the real world like automotive parts, medical devices, or even space industries that require an insane degree of accuracy, Blender for 3D printing can be less accurate, because it is not created for these purposes. But you can do it if you want to, the thing is, it is going to take more time and effort and the results are going less perfect due to the fact that Blender has fewer features for measuring easily, effectively and efficiently like what we can’t find in CAD software. Since It’s more of a sculpting, 3D modeling and animation tool.

But sometimes, the bottleneck is more on 3D printers’ ability to print with accuracy than in the model file’s accuracy.
On the other hand, CAD software such as Solidworks, Inventor, Fusion 360, and others are very good when it comes to accurate industrial design and they can be very fast as well. Also using CAD software you are probably going to face fewer problems exporting your 3D printing ready files. But it is very tough to create any organic models using it, let alone working on something close to what you can create using Blender.
Blender vs CAD software for 3D printing
Blender is very good for 3D printing. Especially if you want to model characters, environment props, machines or anything else organic you can think of. It’s an excellent software. As you learn more about it and get used to its tools and features it will become easier to create 3D printing ready models.

So the answer to the question of whether you should use Blender for 3D printing or other computer-aided design software is going to depend completely on the type of 3D models you are planning to create.
If you need perfect precision when 3D printing mechanical pieces or parts of accurate assemblies then you can use CAD software like SolidWorks, fusion 360 or even some free CAD software for this matter.
6 awesome applications of 3D printing with Blender
Knowing that Blender is a powerful 3D package that has the ability to do almost everything including the ability to print 3D Models, it can actually be used to do a lot of different things outside of 3D printing engineering stuff.
1. Miniature Characters/toys
One of the best applications of Blender for 3D printing actually. It could definitely be used to create a 3D-print ready miniature from start-to-finish, whether you are a beginner or a professional 3D character printer. And there are some artists who use Zbrush in addition to Blender to do final touches. Especially if you have a very complicated character with tens of millions of polygons, but as we said you can do it all in Blender if you want to.

One important difference between video game, animation or film character modeling and 3D-print character modeling is that a 3D-print character model cannot benefit from visual techniques like smooth shading, baking normal maps to a low-poly retopologised model, subdividing only during renders, etc. All the detail that you wish to be present in your printed 3D model, MUST be present in the geometry itself, and that means a very detailed, organic 3D-print model is likely to be far heavier, geometrically, than other kinds of model.
A high-resolution character in a video game might be 20 to 70 thousand polygons after retopology. A very detailed 3D print character might be 20-30 million polys prior to decimation, and 500k-1M polys when sent to the printer.
2. Jewelry

Blender is a good 3D software for designing jewelry, that’s why it is being used for this purpose. You can do it using the tools that modelers and designers usually use. And to make the process easier and to get better results you can use Jewelcraft which is a Blender add-on that will allow you to add gemstones and prongs to the model you have designed. You must have a workable model that you have already drawn up. So basically Jewelcraft helps you to place stones, add prongs and use cutouts to modify your model for jewelry design work and ready it for 3d printing.
3. Entertainment industries

Movie studios and special effects artists are now able to use 3D printing to make concept models, and full-size props, set-pieces, and costumes. It is a very good alternative for spending many hours hand crafting hundreds of pieces. Because they can just use a 3D package whether it be Blender or any other 3D package or sculpting software to get the job done.
4. Architecture

Architects can actually use Blender for 3D printing in different architectural structures made from different materials. In order to offer clients a physical representation of what the building is going to look like. And it can also be done using Architecture computer design software which what architects use for the most part.
5. Interior design
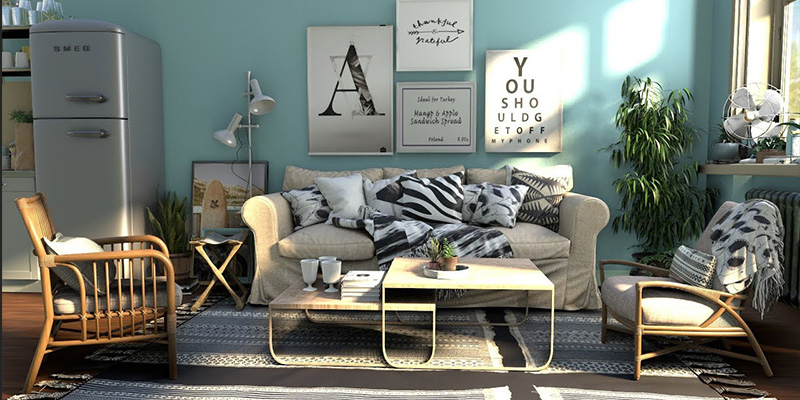

Interior design is a good application of 3D printing since it is cost effective and less time consuming. Because you can just print the 3D models you created in Blender and start bringing your interior design to life. Also, smaller items that are usually custom made can be printed very fast without wasting human labor, time and money during the process.
6. Medicine

Medical care is one of the most important application of 3D printing, one that can literally save lives. It’s mostly notorious in custom medical equipment, prototypes for surgical planning and education, implants and prosthetics, biomaterials and so much more.
Drawbacks of using Blender for 3D printing
While there are many benefits to using Blender for 3D printing, there are also some potential drawbacks to be aware of.
Learning curve
Blender can take some time to learn, particularly for those who are new to 3D modeling. However, with practice and dedication, even beginners can become proficient in using the software. Not to mention the plethora of 3D printing Blender tutorials that can prove to be an efficient way to compensate the learning curve.
Compatibility issues
While Blender is compatible with many 3D printers, there may be compatibility issues with some machines or software. This is something to keep in mind if you’re considering using Blender for your 3D printing projects.
Potential limitations
Depending on your specific needs, Blender may not be the best choice for your 3D printing projects. For example, if you’re looking to create very simple models, there may be other software options that are better suited to your needs.
Conclusion
Blender is a powerful 3D modeling software that can be used to create models for 3D printing, especially for organic models, machines, and environment props. Blender’s flexibility and tools specifically designed for 3D printing make it a great option for hobbyist 3D printers, and even professionals who need to create complex models.
However, for accurate industrial design, specialized CAD software like SolidWorks and Fusion 360 are better suited. Overall, Blender has many applications beyond 3D printing, and is a valuable tool for artists, designers, and creators in various industries.